
Note: The PPTP/L2TP will be deprecated in future firmware. It is strongly recommended to use the improved OpenVPN , which offers more possibility and security. OpenVPN is currently the deFacto standard in Virtual Private Networks.
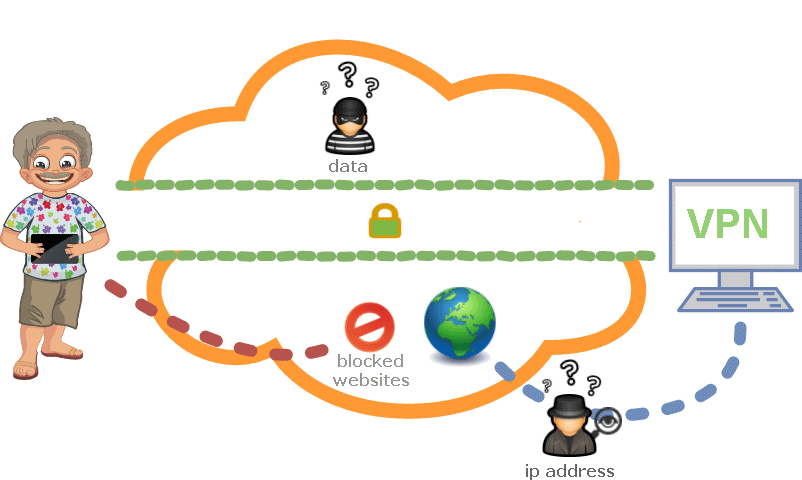
PPTP stands for "Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol." PPTP is a networking standard for connecting to virtual private networks, or VPNs. VPNs are secure networks that can be accessed over the Internet, allowing users to access a network from a remote location. This is useful for people who need to connect to an office network from home or access their home computer from another location.
In Short, PPTP is useful because : -
- hides your original IP address
- allows you to access websites blocked by your local Internet Service Provider and Hotspot providers
- allows you to watch a local TV program when you are in a foreign region
The "point-to-point" part of the term refers the connection created by PPTP. It allows one point (the user's computer) to access another specific point (a remote network) over the Internet. The "tunneling" part of the term refers to the way one protocol is encapsulated within another protocol. In PPTP, the point-to-point protocol (PPP) is wrapped inside the TCP/IP protocol, which provides the Internet connection. Therefore, even though the connection is created over the Internet, the PPTP connection mimics a direct link between the two locations, allowing for a secure connection.
L2TP stands for Layer Two Tunneling Protocol is an extension of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) used by an Internet service provider (ISP) to enable the operation of a virtual private network (VPN) over the Internet. L2TP merges the best features of two other tunneling protocols: PPTP from Microsoft and L2F from Cisco Systems. The two main components that make up L2TP are the L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC), which is the device that physically terminates a call and the L2TP Network Server (LNS), which is the device that terminates and possibly authenticates the PPP stream.
How to create a PPTP/L2TP connection?
To create a VPN connection from the EZhotspot Extender using PPTP/L2TP to a remote server, you need to subscribe to a VPN service or have a private PPTP/L2TP server running.
Most VPN service companies offers an alternative PPTP connection on top of the standard OpenVPN connection.
However, you can easily create a private PPTP server using a Windows® based computer and the knowledge to create a Port Forwarding or DMZ in your ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem router. You may also need a DDNS solution if the IP address provided by your Internet Service Provider changes, also known as dynamically assigned IP address.
For the many reason of the different versions of Windows® Operating System and different brands of ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem routers, it is impossible to give you a detailed explanation of How to Do it, we can only suggest some guides and links below. Before proceeding, you might be cautioned that intermediate computer technology skills are required.
Things to do at the ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem routers
Always check out the possibility on your existing ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem routers. Most Internet Service Providers do not provide you a detailed user guide about your ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem routers. They are only configured that you are ensured of an internet connection to their service. You will need to venture by yourself to understand what your ADSL/Cable/Fiber Modem routers can and will do. If you need to locate them, they are always the gateway address shown in your connecting clients. Type this address in your browser and if you have username and password (usually admin), you have now the possibility to configure the port forwarding or DMZ as needed.
Things to do at the Computer
Check out some of these blogs below to help you create a Windows® PPTP server.
Setup a PPTP server on Windows 10
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows NT®, Windows Server® and Windows VistaTM are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.